What is Design for Disassembly (DfD)?
DfD is an innovative approach in design, manufacturing and construction, emphasising the way buildings, products and interiors are designed and assembled to facilitate easy disassembly and reuse of materials. Unlike traditional manufacturing and construction methods, which often result in significant waste and environmental impact, DfD aims to extend the lifecycle of materials and reduce the overall carbon footprint.
In the context of corporate workplaces, DfD ensures that office interiors and the products that go into them can be reconfigured, relocated, refurbished or recycled with minimal waste and cost, supporting a circular economy where materials are continuously repurposed and reused.
Core Principles
The principles of DfD for interior fit-outs revolve around sustainability and resource efficiency. Key aspects include:
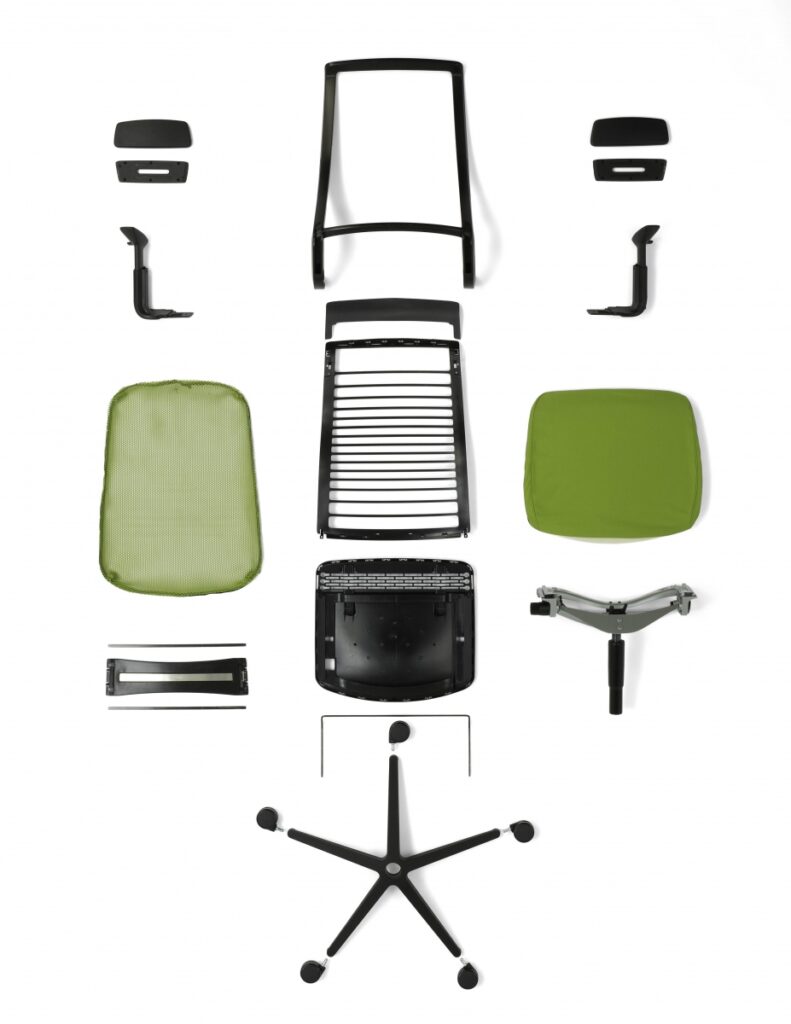
1. Ease of Disassembly: Office products and interiors that are designed to be taken apart without damaging components, facilitating reuse and recycling.
2. Material Selection: Use of materials that are durable, recyclable, and non-toxic to ensure they can be reused in new configurations.
3. Modular Design: Incorporation of modular systems that can be easily reconfigured or replaced.
4. Documentation and Labelling: Thorough documentation of materials and methods used, ensuring future disassembly teams can understand how to disassemble.

Economic Advantages
1. Cost Savings on Renovations: DfD can potentially reduce costs associated with renovations. Since components are designed for easy disassembly, labour and equipment costs involved in these processes can be lower.
2. Asset Value Preservation: Office interiors designed for disassembly can potentially retain higher value over time as materials and components can be sold or reused, creating a secondary market for materials, components and furniture.
3. Tax Incentives and Credits: Governments are increasingly offering tax incentives and credits for sustainable building practices, which can improve the financial performance of corporate real estate investments.
Environmental Benefits
1. Reduction in Fit-Out Waste: DfD significantly reduces the volume of waste generated during office renovations and fit-outs. This helps companies meet sustainability goals and comply with regulations.
2. Lower Carbon Footprint: By reusing materials, the carbon emissions associated with manufacturing new materials are reduced. This contributes to the overall reduction of the office’s carbon footprint.
3. Resource Conservation: DfD promotes the efficient use of natural resources, aligning with global sustainability trends and corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals.
Social and Corporate Responsibility
1. Enhanced Corporate Image: Companies that adopt DfD principles can enhance their reputation as leaders in sustainability, attracting customers, investors, and employees who prioritise environmental responsibility.
2. Compliance with Regulations: As sustainability regulations become more stringent, DfD can help companies stay ahead of compliance requirements, avoiding potential fines and legal issues.
Importance of Design, Product Selection, and Construction Choices in Interior Fit-Outs
For DfD to be effectively implemented in corporate workplace interior fit-outs, careful consideration must be given to design, product selection, and construction methods. Each of these components plays a critical role in ensuring that office interiors can be efficiently disassembled and materials reused.

Design Considerations
1. Modularity: Designing office interiors with modular components allows for easy replacement and reconfiguration. This flexibility can extend the life of the interior fit-out and make future renovations less disruptive and costly.
2. Standardisation: Using standardised components and connections simplifies the disassembly process and ensures that materials can be easily repurposed.
3. Documentation: Comprehensive documentation of the office interior’s design and materials is essential for future disassembly. This includes labelling materials and providing detailed manuals.
Product Selection
1. Recyclability and Reusability: Selecting materials that can be easily recycled or reused is fundamental to DfD. This includes metals, certain plastics, and sustainably sourced wood.
2. Non-Toxic Materials: Avoiding materials that release toxins during disassembly or recycling ensures the health and safety of workers and reduces environmental impact.
3. Durability: Durable materials reduce the frequency of replacements and maintenance, contributing to the interior fit-out’s overall sustainability.
Construction Methods
1. Reversible Connections: Using bolts, screws, and other reversible fasteners instead of adhesives and welds facilitates easier disassembly.
2. Pre-fabrication: Pre-fabricated components can be assembled and disassembled with less waste and greater precision.
3. Minimising Mixed Materials: Avoiding the use of composite materials that are difficult to separate at the end of their lifecycle ensures that more materials can be reused or recycled.
Overall, Design for Disassembly represents a transformative approach to office interior design, construction and procurement, offering significant benefits for corporate workplaces. By prioritising sustainability, resource efficiency, and economic value, DfD aligns with the growing emphasis on environmental responsibility and long-term asset management.
As sustainable practices are now at the forefront of the design and construction process, DfD naturally plays a crucial role.
![The [RE]Search Co.](https://re-search.co/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/The-RE-Search-Co-Orange_Grey-png-350x51.avif)